Automation
The Best Devices for a Smart home – and what to do with them
Published
3 years agoon
By
Jean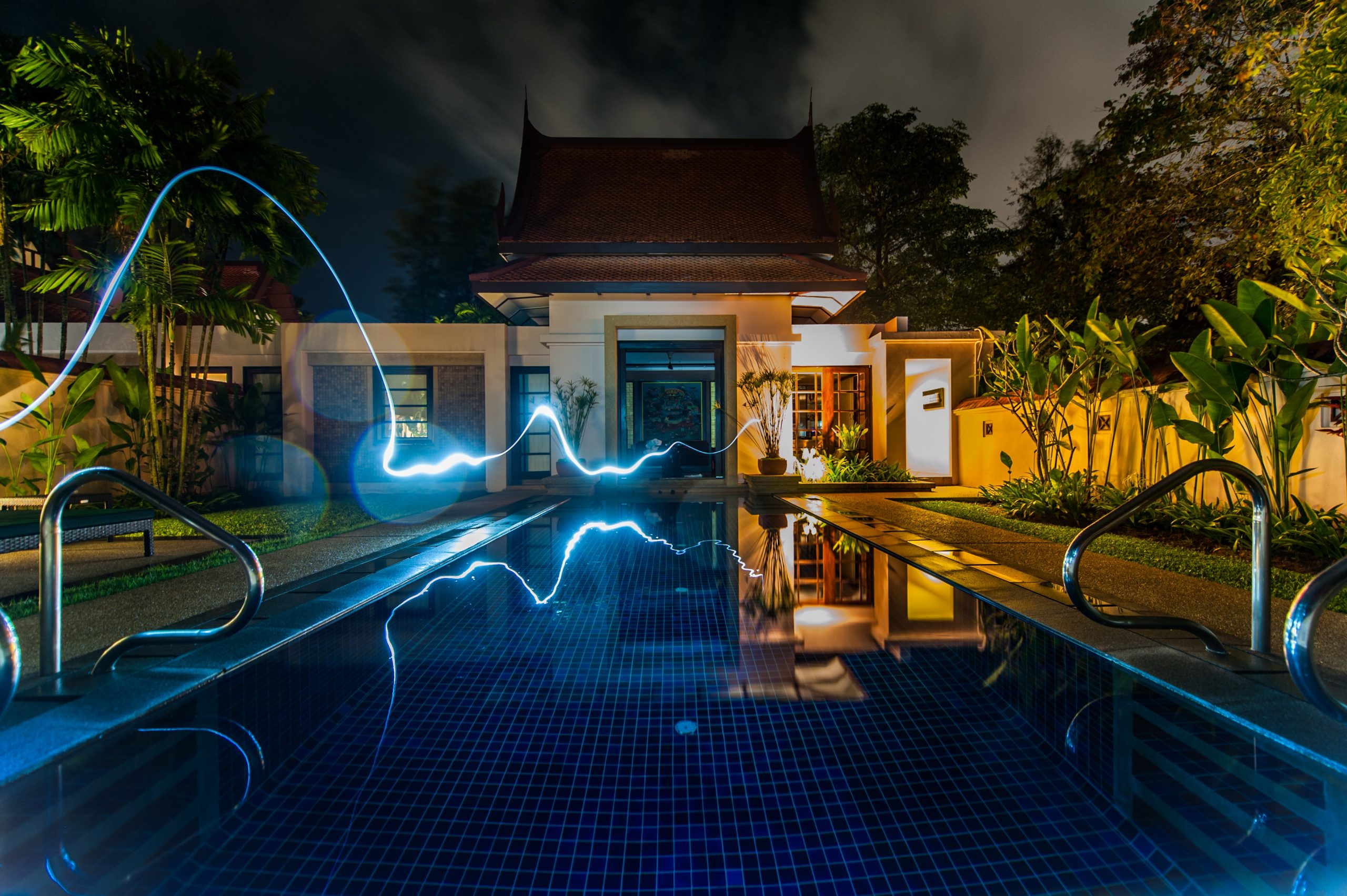
Smart homes are here to stay. Right now, you can decide whether you want to turn your lights on manually or with your voice. Already, household electronics are being designed for Internet of Things so that one day soon, your home appliances and fittings will automatically adjust themselves to fit in with your lifestyle.
These devices will collect information, analyze the information, and respond to this information. This will make your home a smart home.
The promise of smart homes is an easier life as well as more efficient use of scarce resources like water and energy.
Defining Smart Homes
When the gadgets in your home are connected wirelessly, they operate in smart ways. The lights might come on when you walk into your home. Your entire home may even be able to secure itself at night without you doing anything – doors locking, curtains closing, thermostat dialing down, and lights going off. The whole routine goes on without you lifting a finger.
‘SMART’ stands for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology, which means that a smart home is not just automated – it actively gathers information and amends its behavior accordingly. All these are possible features of an automated home. Pre-determined triggers prompt the home to do things. For example, lights can go off at a certain hour, or in response to a verbal instruction. Thermostats can dial up or down depending on the temperature. Soon, smart homes will feature cutting-edge artificial intelligence.
All the home automation options available rely on programming to connect all your devices into a truly smart home. Programs are designed to respond to voice commands, the location of the home owner, and other triggers.
Smart Devices for a Smart Home
Smart Lighting
Smart lighting is a good place to start if you want to achieve a smart home. Besides energy savings and convenience, smart lighting instantly makes your home cool. Smart bulbs can adjust intensity, oscillate between warm and white, even change color. Smart switches connect all the lights so that they are easy to control.
Smart Locks
Smart locks add convenience and let in visitors securely. They save you from the hassle of carrying keys – or hiding them under a rug. A fingerprint, code, or phone is enough to let you in. They can also trigger other features like light or shut everything down upon departure.
Smart Heating
With a little help from your phone, the locks, or presence sensors, your thermostat can know whether you are home and turn itself down or up. This saves energy. The thermostat can also adjust to more heat from the sun.
Smart Security
You may not have CCTV, but a smart home allows you to keep watch using cheap wifi enabled cameras that are motion activated. They are simple enough for anyone to install and use.
Burglars are more likely to avoid a home under surveillance because they provide evidence. They help you watch your pets, elders, or teenagers home.
The video doorbell is a special device that functions like voicemail on your door. Visitors who turn up in your absence can record a video message for you.
With a smart security system, you can monitor your home from anywhere using your smartphone.
Smart Entertainment
Smart TVs are already present in most homes. Smart speakers are also super cheap and serve such a variety of uses as to be indispensible.
They can play a specific song on demand even enable your TV to receive voice commands.
You can connect your speaker to Alexa, Google, or Siri and it will take instructions like read the news or set a timer in the kitchen.
Why you should think about a Smart Home
There are three major reasons why people invest in smart homes. Smart homes offer efficiency, security, and convenience.
Convenience
The interconnectedness of devices in a smart home makes it possible to manage your home more effortlessly. You can create a morning routine that involves setting off your alarm, getting the coffee maker started, turning on the lights, tuning into your preferred radio show, and starting off the shower.
Security
With cameras and an internet connected smart home, you can always monitor the goings on while you are away. Someone showing up at your front door, any movement in the home, doors opening, can all trigger smart sensors to alert you. Smart locks can even tell you who it was that came in through the door, making it possible to keep tabs on your kids.
Energy Efficiency
The smart thermostat drastically reduces energy consumption. But every aspect of the smart home contributes to energy efficiency. You can remotely manage your energy intensive domestic gadgets using a smart phone. You can ensure that rooms are only warmed and lit when they are being used. Smart plugs monitor home energy consumption and allow you to discern opportunities for cutting costs.
How the Smart Home Works
Smart devices are easy to install and use because they depend on wireless connections. You will not have to lay down untidy cable wires across your home. They run on Z-Wave, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Wi-Fi, or Thread protocol most of the time. These wireless radio protocols make it possible for your electronic devices to communicate with each other and with the Cloud.
In a smart home, devices may communicate with each other through a hub within the home and only use the Cloud to store data and process commands. This data includes video footage, photographs, etc. This data is relayed to the Cloud over Wi-Fi.
Most devices need to be controlled and set up via an app installed on a tablet/smart phone. The app enables smart home users to interact with their devices at home. They can schedule things or hook up to their smart home network to automate your home and put in place routines.
Choosing a Smart Home Ecosystem
You can buy smart gadgets like video doorbells that can do their job autonomously but a smart home is a lot more than just a single gadget. Your gadgets have to coordinate with each other to create routines, automate functions, and generally adjust to your lifestyle.
You can achieve this with a Smart Home Ecosystem which connects to all your home devices and allows them to be programmed, manipulated, and coordinated to create routines.
There are now four leading smart home ecosystems in the market: Homekit from Apple, Home from Google, Alexa from Amazon, and SmartThings from Samsung. They are all easy to install and set up. You do not need to hire someone else to install them, unless you want to.
You are already on the right track if you have a digital assistant combined with an ecosystem like Apple’s Homekit. To start setting up a smart home, you have to first have a clear picture of your priorities. Elements like lighting, temperature, security, and entertainment all need to be modified to fit in with your lifestyle as it is. Your lifestyle and preferences should inform your Smart Home design.
Start by looking for devices that enable you to control the elements you need to control, like heating. Once you have the device, you now need to put in an ecosystem to support the devices. Anything else will come as an add-on.
Most devices are capable of functioning within multiple ecosystems. You will not have to spend too much money on hardware. And apps are free on the Playstore or Applestore. You can switch from one ecosystem to another or even use them simultaneously. They are not designed to be mutually exclusive.
HomeKit from Apple
Pros and Cons of HomeKit from Apple:
HomeKit is simple and reliable, as well a secure solution for people who care about their privacy. The HomeKit processes all your data locally and encrypts it before uploading it to the Cloud. This ensures the privacy of your personal information.
Apple’s HomeKit is ideal for Apple users because it works with iPhones, Macs, iPads, and Apple Watches. Siri provides voice control. The HomeKit runs on Thread, WiFi, and Bluetooth.
The downside of working with HomeKit is that it is only compatible with iPhones and iPads, not Android devices. Users will need to deploy the HomePod Mini, Apple TV or other Apple Hub. This drives up the cost of the Apple HomeKit.
Pros and Cons of Alexa from Amazon:
Alexa is named for the voice assistant called Alexa. Alexa is affordable and offers the widest range of compatibility with the devices in your home. This range has been enhanced by the addition of Zigbee radio to Alexa’s Echo speaker (it already has Bluetooth and Wifi). This means that it works well with everything from light bulbs to motion sensors.
Alexa makes it easier to create a voice-control enabled smart home system because so many affordable smart speakers, thermostats, displays, and light switches come with it already inbuilt.
Even though it is compatible with more devices than HomeKit, there are some devices that do not necessarily work properly with Alexa. Do not purchase any electronic device before first testing how it works with Alexa. One more downside to Alexa is that it is harder to access using a smartphone compared to the other smart home solutions.
Pros and Cons of Google Home from Google:
The app for controlling this smart home system is also aptly called Google Home and you can use your smart phone to run it. Google Home’s answer to Alexa is the Google Assistant and it enables a voice controlled home. You can operate the Google Assistant from anywhere because it is in your smart watch or Android phone.
Google offers two smart displays: Nest Hub Max and Nest Hub with a touchscreen for a control panel. You do not need your voice to adjust your thermostat, lights, speakers, and locks.
The range of home devices that work with Google is growing fast, but still relatively small. Google Home does not offer users the option of using sensors to trigger routines. It only has voice command, phones, and automated schedules. Plus, Google Home only has Thread, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. It does not support Z-Wave or Zigbee.
Pros and Cons of SmartThings from Samsung:
SmartThings is one of the premier smart home solutions and is compatible with more smart home gadgets than the others. This includes most Samsung appliances, of course. SmartThings is capable of controlling Wi-Fi as well as Zigbee and Z-Wave devices.
This is an advantage because Z-Wave can work with smaller devices using less power. And it responds faster because it communicates to its hub and not the Cloud.
SmartThings can work with Alexa as well as Bixby voice assistant from Samsung. You can use both.
The downside is that SmartThings is the most complex system, especially when paired with Zigbee and Z-Wave devices. This is the downside of working with such a powerful and multifaceted system.
Building your own Smart Home System
What if you want a Smart Home but do not want to give tech companies access to your home? You could consider creating your own smart home. Use open-source software for your home assistant and Raspberry Pi.
This approach calls for the type of people who enjoy the challenge of building computers. It is rewarding and allows you to customize it and protect your private information.
Adding Voice Control to your Smart Home
All smart home systems can be voice-controlled. You should not have to get up from your couch to turn off the light (or adjust the temperature) after installing a smart home.
A smart speaker will give you the best voice control. Each of these systems has compatible speakers which have radio for wireless protocols. These speakers do more than just add voice control.
Smartphones, smart watches, tablets, and smart speakers have digital assistants. Only Siri from Apple works from a desktop computer.
Voice control works when you equip each room with a speaker which will automatically know which room it is placed in.
Putting it all Together
After installing your smart home gadgets, you want to create routines and scenes and automate functions. Thankfully, the ecosystems we have discussed are nearly similar.
You start by picking a trigger which will prompt the automated functions. The trigger could be your location, the time, or an event – like a door being opened.
You then decide on when or the ‘conditions’ under which these functions will happen. It could be daily or on weekends, or when you are away. You could put in place one condition or multiple conditions.
You can now decide what happens next. For example when someone opens a door, a camera comes on or the thermostat is adjusted. Multiple actions can happen at once. They are called a Scene.
To trigger a scene, you may use the app or voice command. For example, a ‘movie’ scene will turn up heat, dim lights, and start Netflix.
Here are some routines you can start with: Goodbye, Good Morning, Welcome home, and Goodnight. These are all fully customizable.
You may like
-

AI Breakthrough: New System Detects Early Signs of Heart Disease, Revolutionizing Preventive Care
-


Microsoft’s Copilot AI: Revolutionizing Windows 11 and the Future of Personal Computing
-


SpaceX’s Starship Achieves Milestone with Successful ‘Chopstick’ Catch in Fifth Test Flight
-


Apple’s Vision Pro: A New Frontier for Developers in Spatial Computing
-

AI Breakthrough: New Model Revolutionizes Protein Structure Prediction
-

Iron-Air Batteries: The Future of Home Energy Storage
Automation
Revolutionizing Industrial Automation: Vention’s Collaboration with NVIDIA AI
Published
5 months agoon
June 2, 2024By
Jean
In a groundbreaking move set to redefine the landscape of industrial automation, Vention has announced a strategic partnership with NVIDIA, leveraging advanced artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to democratize the sector. This collaboration, centered on Vention’s cloud-based Manufacturing Automation Platform (MAP), aims to bring sophisticated automation solutions to a broader range of businesses, thereby enhancing efficiency and productivity across industries.
The Dawn of Accessible Automation
Vention’s mission to make industrial automation more accessible is not new. The company has been a pioneer in offering customizable and scalable automation solutions that cater to the unique needs of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). By integrating NVIDIA’s AI technologies into its platform, Vention is poised to take this mission to new heights. The integration will empower users with advanced capabilities such as predictive maintenance, real-time data analytics, and enhanced machine learning, making sophisticated automation tools available to businesses that previously lacked the resources to implement such technologies.
Harnessing the Power of AI
The core of this initiative lies in the integration of NVIDIA’s AI technologies, renowned for their robustness and versatility. NVIDIA’s AI platform is designed to handle vast amounts of data and perform complex computations rapidly, making it an ideal fit for industrial applications. By embedding these capabilities into Vention’s MAP, businesses can now harness the power of AI to optimize their operations. For instance, predictive maintenance powered by AI can foresee potential equipment failures before they occur, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Similarly, real-time data analytics can provide actionable insights, enabling businesses to make informed decisions swiftly.
Empowering the Manufacturing Sector
The collaboration is set to benefit a wide array of industries, particularly manufacturing, which stands to gain immensely from advanced automation solutions. The manufacturing sector has long been a cornerstone of economic growth, but it has also faced challenges such as high operational costs and inefficiencies. With the introduction of AI-driven automation, manufacturers can streamline their processes, improve product quality, and reduce operational costs. This transformation is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in a global market that is increasingly driven by technology and innovation.
AI and the Future of Work
One of the significant implications of this partnership is its potential impact on the workforce. As automation becomes more prevalent, there is a growing concern about the displacement of jobs. However, Vention and NVIDIA’s approach is centered on augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them. By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, workers can focus on more complex and creative aspects of their jobs. Additionally, the need for skilled workers to manage and maintain these advanced systems will create new employment opportunities, fostering a more skilled and knowledgeable workforce.
Collaboration with Industry Leaders
The announcement has garnered attention from industry leaders and experts who recognize the transformative potential of this partnership. According to IndustryWeek, integrating AI into industrial automation represents a significant leap forward in the evolution of manufacturing technologies. Furthermore, the International Federation of Robotics emphasizes the role of AI in enhancing the capabilities of robotic systems, which are integral to modern manufacturing processes.
Sustainability and Efficiency
Another critical aspect of this collaboration is its contribution to sustainability. As businesses strive to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt more environmentally friendly practices, AI-driven automation offers viable solutions. Efficient resource management, reduced waste, and optimized energy consumption are some of the ways through which AI can help businesses achieve their sustainability goals. This alignment with environmental objectives not only benefits the planet but also enhances the reputation and compliance of businesses in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
To illustrate the practical benefits of this collaboration, consider the case of a mid-sized manufacturing company that implemented Vention’s AI-enhanced MAP. By utilizing predictive maintenance, the company was able to reduce its downtime by 30%, resulting in significant cost savings and improved productivity. Additionally, real-time data analytics provided insights into production bottlenecks, allowing the company to streamline its processes and increase output. These tangible benefits highlight the potential of AI-driven automation to revolutionize industrial operations.
The Road Ahead
As Vention and NVIDIA continue to innovate and expand their collaboration, the future of industrial automation looks promising. The integration of AI into manufacturing processes is just the beginning. Future developments may include more sophisticated machine learning algorithms, greater interoperability between different automation systems, and further enhancements in data analytics capabilities. These advancements will continue to drive efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in the industrial sector.
Conclusion
The partnership between Vention and NVIDIA marks a significant milestone in the journey towards democratizing industrial automation. By making advanced AI technologies accessible to a broader range of businesses, this collaboration has the potential to transform industries, enhance efficiency, and promote sustainability. As businesses embrace these innovations, they will be better equipped to navigate the challenges of the modern industrial landscape and thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
For more detailed insights into this collaboration, visit the official press release.
Automation
IBM Acquires HashiCorp for $6.4 Billion, Bolstering Its Multicloud Automation Capabilities
Published
6 months agoon
April 28, 2024By
Jean
In a strategic move to enhance its multicloud automation capabilities, IBM has acquired HashiCorp for $6.4 billion, signaling a significant expansion of its hybrid cloud strategy. This acquisition underscores the growing importance of cloud technology in the digital economy and represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of enterprise computing.
HashiCorp, a company long known for its robust cloud infrastructure automation tools, has established itself as a critical player in the cloud ecosystem. With technology agreements with all major cloud providers, including Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, HashiCorp brings a wealth of expertise and technology to IBM’s portfolio. The acquisition is a strategic fit for IBM, enhancing its existing capabilities and providing comprehensive solutions across various cloud environments.
During a conference call announcing the deal, Arvind Krishna, IBM’s chairman and chief executive officer, highlighted the synergies between the two companies. “HashiCorp is a company we have partnered with for a long time and believe is a tremendous strategic fit with IBM,” Krishna stated. He pointed out the increasing challenges that enterprise clients face in managing sprawling infrastructure applications spread across public and private clouds, as well as on-premises environments.
The timing of this acquisition aligns with the rapid deployment of generative AI and traditional workloads, which necessitates more sophisticated infrastructure strategies. Developers are currently navigating an increasingly heterogeneous, dynamic, and complex landscape, making HashiCorp’s solutions more relevant than ever. “As generative AI deployment accelerates alongside traditional workloads, developers are working with increasingly heterogeneous, dynamic, and complex infrastructure strategies,” Krishna explained.
HashiCorp’s flagship product, TerraForm, stands out as the industry standard for infrastructure automation in these environments. With a focus on security, which is a top concern for every enterprise today, TerraForm offers tools that significantly ease the complexities of managing hybrid and multicloud environments. According to Krishna, “TerraForm is the industry standard for infrastructure automation for these environments with security top of mind for every enterprise.”
The integration of HashiCorp will extend the capabilities of IBM’s existing hybrid cloud offerings, particularly those provided by Red Hat. This will enable IBM to offer end-to-end automated infrastructure and security lifecycle management, further enhancing its competitive edge in the cloud services market.
This acquisition also reflects a broader industry trend where major technology companies are increasingly seeking to consolidate their positions in the cloud sector through strategic acquisitions. Companies are recognizing the need to provide integrated solutions that can handle the complexity of modern IT environments, which often span multiple cloud providers and incorporate a mix of legacy and cloud-native applications.
As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, the demand for tools that can automate and secure cloud infrastructures is expected to grow. IBM’s acquisition of HashiCorp is a clear indication that the company is looking to lead this wave of transformation, providing its clients with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of digital transformation.
For further information on IBM’s cloud strategy and offerings, you can visit their official website. This acquisition is not only a significant milestone for IBM but also for the broader cloud technology ecosystem, marking a new chapter in the way enterprises will manage their digital infrastructures in the future.
Automation
The Transformative Role of Automation Technology in Banking: Navigating the Future with Efficiency and Compliance
Published
7 months agoon
April 10, 2024By
Jean
In an age where technological progression sets the tempo for industries across the board, the banking sector finds itself at a crossroads between tradition and innovation. Automation technology, a force majeure in this digital symphony, promises a future where efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction are not just goals but realities. PaymentsJournal’s recent exploration into this dynamic arena highlights how financial institutions are increasingly turning to automation to not only streamline operations but also to navigate the choppy waters of regulatory compliance with agility and foresight.
Embracing Change Amidst Regulatory Tides
The banking landscape is no stranger to regulation; if anything, it’s a domain where regulatory frameworks dictate the rhythm of progression. The impending modernization of the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) and the introduction of Dodd-Frank 1071 underscore a regulatory environment in flux, one that demands adaptability and forward-thinking strategies from financial institutions. The CRA, a bedrock of equitable lending practices, is poised for an overhaul to align with the digital age, ensuring that banks continue to meet the evolving needs of their communities. On the other hand, Dodd-Frank 1071 aims to shine a light on small business lending practices, with a particular focus on transparency for businesses owned by women and minorities.
The essence of these regulatory updates transcends mere compliance; they represent a shift towards a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient banking ecosystem. However, the road to adherence is fraught with challenges, primarily due to the manual and labor-intensive processes entrenched in the sector. This is where automation technology, with its promise of precision and efficiency, steps in as a pivotal ally for banks navigating the compliance maze.
Automation: A Lever for Efficiency and Compliance
The role of automation in banking transcends operational efficiency. It’s a strategic imperative that addresses a spectrum of challenges, from reducing manual errors to enhancing customer experiences. Tools and systems like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) are not just buzzwords but integral components of a bank’s arsenal to streamline complex processes and improve decision-making. The Federal Reserve’s insights into banking automation underscore the transformative potential of these technologies in risk management and compliance, highlighting how they can offer real-time monitoring and analysis of transactions to detect anomalies and mitigate fraud.
The efficiency brought about by automation is particularly relevant in the context of compliance. Financial institutions are well-acquainted with the resource-intensive nature of manual compliance processes. Automation offers a reprieve by streamlining data collection and reporting, thereby ensuring accuracy and reducing the likelihood of errors that can lead to regulatory penalties. Moreover, the dynamic nature of regulatory frameworks necessitates a degree of agility that only automated systems can provide. These systems offer continuous monitoring and adaptability to regulatory changes, ensuring that banks remain on the right side of compliance.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Banking with Automation
The journey towards fully automated banking processes is not without its hurdles. Questions about data security, privacy, and the digital divide persist. Yet, the trajectory is clear: automation is not just an option but a necessity for banks aiming to thrive in an increasingly digital and regulated world. Industry leaders and regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of collaboration between banks and technology providers to navigate these challenges effectively.
The transition towards automation in banking, prompted by regulatory changes and operational efficiencies, is more than a technological upgrade. It’s a reimagining of what banking can be in the 21st century: more accessible, efficient, and inclusive. As financial institutions continue to harness the power of automation technology, they pave the way for a future where banking is not just about transactions but about fostering growth, inclusivity, and innovation in the communities they serve.
In essence, the transformative role of automation in banking is a narrative of progress. It’s a story of how technology, when aligned with strategic vision and regulatory compliance, can redefine the banking experience for institutions and customers alike. As the sector stands on the brink of this digital revolution, the promise of a more efficient, compliant, and customer-centric banking future seems not just plausible but inevitable.
Trending
-

 Home4 years ago
Home4 years agoBest Science Board Games
-

 Medical4 years ago
Medical4 years agoPatients could Start to Monitor their Vision Remotely from Home
-

 Gadgets4 years ago
Gadgets4 years agoNew to 3D Printing? Here are 7 Tips
-
Medical4 years ago
IVF gets Better with AI
-
Medical4 years ago
Four-Week Memory Test that could predict the Risk of Alzheimer’s
-

 Environment4 years ago
Environment4 years agoFarming Could be Transformed by Self-Watering Soil
-

 Medical4 years ago
Medical4 years agoScientists will Soon spot Diseases and find exoplanets with super Tiny photonic devices
-

 Energy4 years ago
Energy4 years agoHere’s Why Your Home Needs a Backup Generator