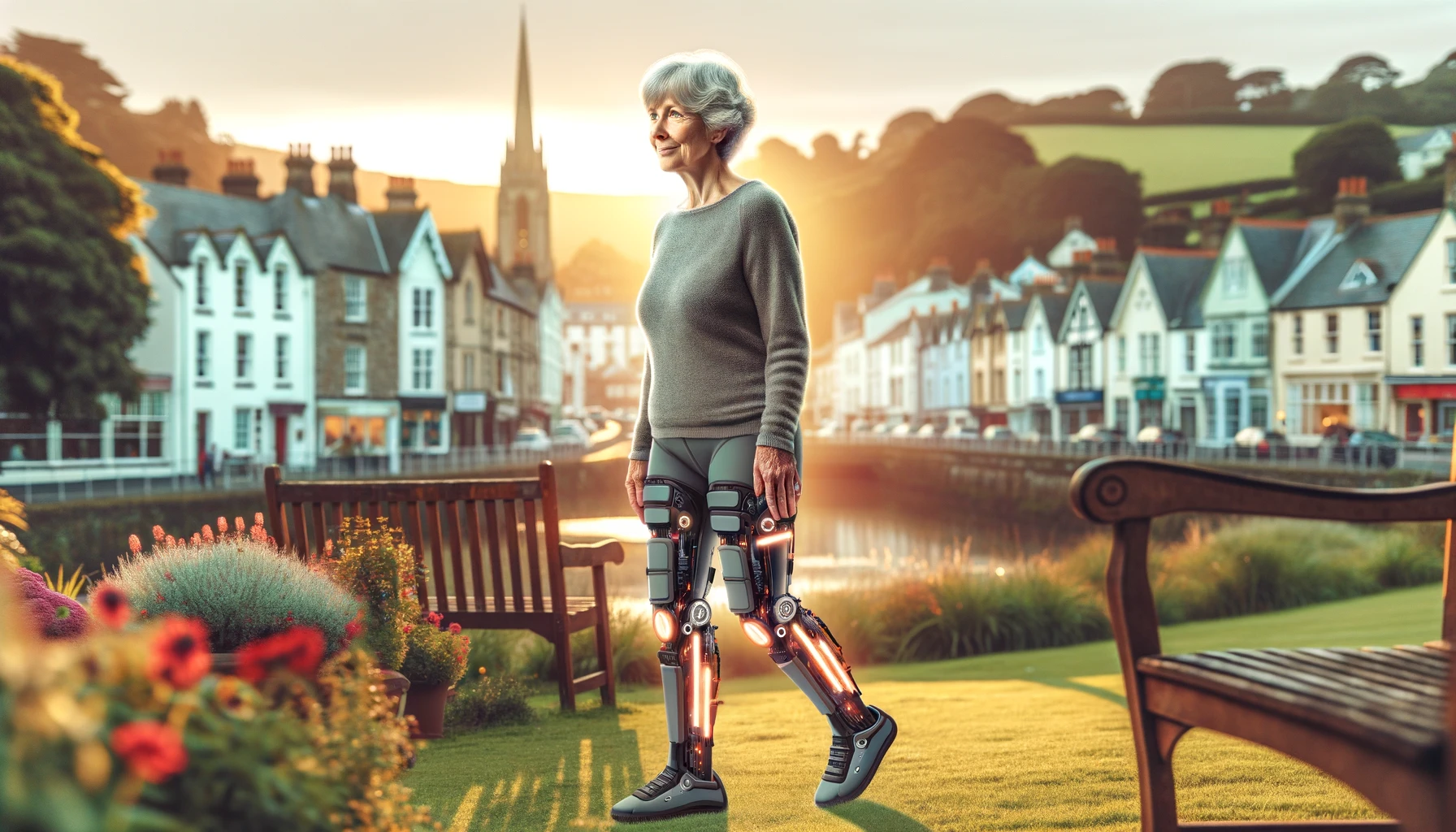
In the quaint town of Penarth, Vale of Glamorgan, a remarkable story of resilience and technological innovation is unfolding. Julie Lloyd, a 65-year-old stroke survivor, is relearning to walk, aided by a groundbreaking piece of technology: trousers powered by artificial intelligence (AI). This pioneering trial in the UK marks a significant leap in medical technology, offering new hope to stroke victims worldwide.
The Breakthrough in Stroke Rehabilitation
Julie’s journey is not just a personal triumph but a beacon of hope for millions affected by strokes. According to the World Health Organization, strokes are the second leading cause of death globally, and the leading cause of acquired disability among adults. The road to recovery is often long and arduous, with traditional rehabilitation methods providing varying degrees of success.
The AI-powered trousers represent a paradigm shift in rehabilitation technology. As Julie puts it, “I really feel this is the breakthrough for stroke victims that has been much and long awaited for.” This sentiment echoes the sentiments of many in the medical community who have long sought more effective ways to aid stroke recovery.
How the Technology Works
The AI trousers are a marvel of modern engineering and medical science. They function by using a series of sensors and motors that work in tandem with the wearer’s movements. This technology is not just about physical support; it’s about enhancing the body’s natural ability to relearn movements. The AI component analyses the wearer’s gait, providing real-time adjustments to improve walking patterns, much like a physical therapist would.
This approach is grounded in the concept of neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. By assisting in the correct movement patterns, the trousers help the brain to ‘relearn’ walking, potentially speeding up the recovery process.
The Impact on Stroke Rehabilitation
The implications of this technology are vast. For stroke survivors, the journey to recovery can be filled with frustration and despair. Traditional rehabilitation methods can be slow and, at times, ineffective. The AI trousers offer a more dynamic and responsive form of therapy that could revolutionize how we approach stroke rehabilitation.
In a study conducted by the American Stroke Association, it was found that early and individualized rehabilitation can significantly improve outcomes for stroke survivors. The AI trousers align perfectly with this philosophy, offering a tailored rehabilitation experience that adapts to the individual’s needs.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the promise, the road ahead for AI in medical rehabilitation is not without challenges. Cost and accessibility are significant concerns. Cutting-edge technology often comes with a high price tag, potentially putting it out of reach for many who could benefit from it.
Moreover, there’s the challenge of integrating such technology into existing healthcare systems. As noted by experts in healthcare technology, the adoption of new medical technologies often faces hurdles in terms of regulatory approval, practitioner training, and patient acceptance.
However, the future looks bright. As AI and robotics continue to advance, we can expect these technologies to become more affordable and widespread. The potential for AI to aid in various aspects of healthcare, from diagnosis to treatment and rehabilitation, is enormous.
Conclusion
Julie Lloyd’s story is just the beginning. As we stand on the cusp of a new era in medical technology, the possibilities are endless. The AI-powered trousers are more than just a piece of technology; they are a symbol of hope and a testament to human ingenuity. For stroke survivors around the world, this could be the dawn of a new day in rehabilitation, one where technology and human resilience come together to create new possibilities.

 Home3 years ago
Home3 years ago
 Medical3 years ago
Medical3 years ago
 Gadgets3 years ago
Gadgets3 years ago
 Environment3 years ago
Environment3 years ago
 Medical3 years ago
Medical3 years ago
 Energy3 years ago
Energy3 years ago